Table of Contents
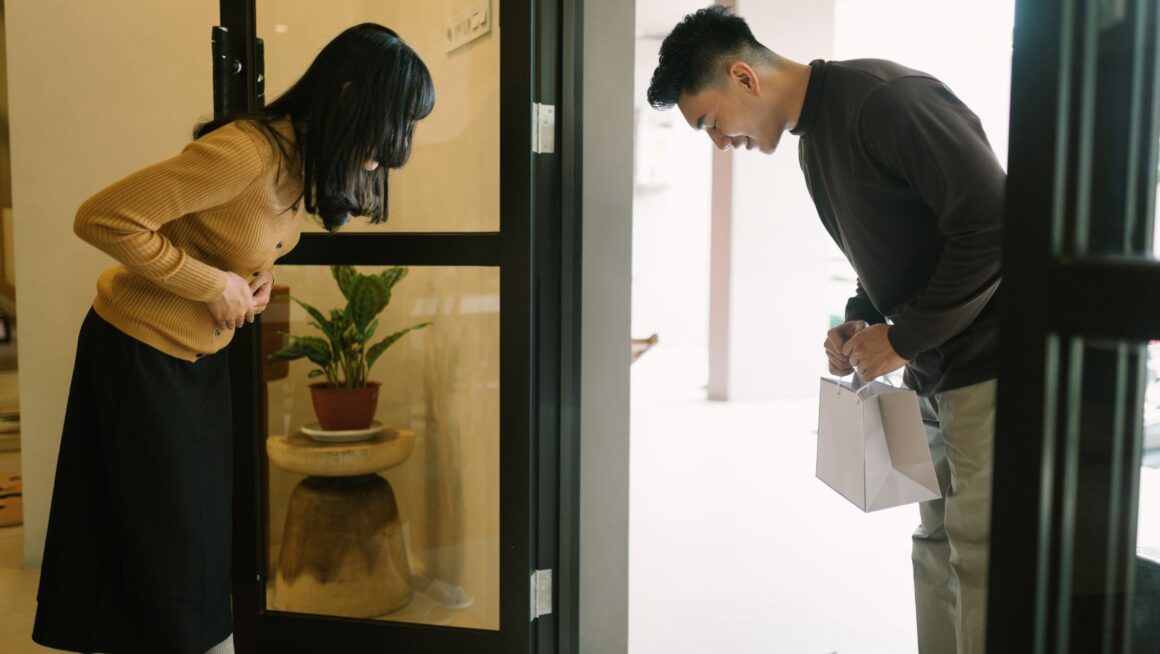
 In the intricate dance of social interactions, proper decorum or tata krama often takes the lead. It’s not just about knowing which fork to use at a formal dinner, but understanding how our actions could impact those around us. This article delves into various examples of how tata krama is applied in behavior, providing a glimpse into the fascinating world of etiquette. From the bustling streets of Jakarta to the serene villages of Bali, the implementation of tata krama is a common thread that binds the diverse Indonesian culture.
In the intricate dance of social interactions, proper decorum or tata krama often takes the lead. It’s not just about knowing which fork to use at a formal dinner, but understanding how our actions could impact those around us. This article delves into various examples of how tata krama is applied in behavior, providing a glimpse into the fascinating world of etiquette. From the bustling streets of Jakarta to the serene villages of Bali, the implementation of tata krama is a common thread that binds the diverse Indonesian culture.
Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah
 Consistent application of tata krama in behavior, makes societal interactions harmonious. For instance, in Javanese culture, the implementation of ‘tata krama’ dictates that one lowers his gaze when passing older people—a sign of respect. Communication also exemplifies this, with formal language adopted in conversations with elders. Bali, on the other hand, showcases ‘tata krama’ in community meetings called Banjar. People sit lower than the presiding leaders, exhibiting deference to authority.In educational settings, students show ‘tata krama’ by standing up when teachers enter classrooms. They use polite language, add “Pak” or “Bu” before teachers’ names, and request for permission before leaving—an embodiment of discipline and respect.
Consistent application of tata krama in behavior, makes societal interactions harmonious. For instance, in Javanese culture, the implementation of ‘tata krama’ dictates that one lowers his gaze when passing older people—a sign of respect. Communication also exemplifies this, with formal language adopted in conversations with elders. Bali, on the other hand, showcases ‘tata krama’ in community meetings called Banjar. People sit lower than the presiding leaders, exhibiting deference to authority.In educational settings, students show ‘tata krama’ by standing up when teachers enter classrooms. They use polite language, add “Pak” or “Bu” before teachers’ names, and request for permission before leaving—an embodiment of discipline and respect.
Understanding the Concept: Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah
Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah translates to Examples of the Implementation of Etiquette in Behavior in English. This term spotlights the practical application of ‘tata krama’ in actions and character, holding cultural significance in Indonesian societies.
What does Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah Mean?
 Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah portrays the embodiment of ‘tata krama’ in day-to-day behavior. It’s an Indonesian phrase that combines specific elements:
Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah portrays the embodiment of ‘tata krama’ in day-to-day behavior. It’s an Indonesian phrase that combines specific elements:
- ‘Contoh’ means examples,
- ‘Penerapan’ relates to implementation or application,
- ‘Tata krama’ signifies etiquette or proper conduct,
- ‘Dalam’ translates to in,
- ‘Bersikap’ stands for behavior, and
- ‘Adalah’ is the Indonesian word for ‘is’.
Thus, it reflects the enactment of ‘tata krama’ or proper manners in Indonesian societies, where cultural norms are observed, and specific behavioral expectations respected.
The Cultural Significance of Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah
 The assertion of Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah embraces a culturally significant meaning in Indonesia’s social fabric. It’s paramount for enhancing interpersonal interactions and harmony. The phrase describes not only basic etiquettes such as showing respect to elders or behaving well in public places but also embraces broader societal values such as honesty, integrity, harmony, and unity.Incorporating these behaviors or customs daily reaffirms societal bonds, reduces conflicts, and promotes peace — a testament to the cultural essence of ‘tata krama’.
The assertion of Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah embraces a culturally significant meaning in Indonesia’s social fabric. It’s paramount for enhancing interpersonal interactions and harmony. The phrase describes not only basic etiquettes such as showing respect to elders or behaving well in public places but also embraces broader societal values such as honesty, integrity, harmony, and unity.Incorporating these behaviors or customs daily reaffirms societal bonds, reduces conflicts, and promotes peace — a testament to the cultural essence of ‘tata krama’.
The Importance of Appropriate Behavior in Society
 The cultural importance of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah underscores the significance of appropriate behavior in any society. It structures the order of daily interactions, expressing respect for individuals, their roles, and the community as a whole. It ensures a peaceful harmony within each interaction, marking a society that thrives on unity.
The cultural importance of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah underscores the significance of appropriate behavior in any society. It structures the order of daily interactions, expressing respect for individuals, their roles, and the community as a whole. It ensures a peaceful harmony within each interaction, marking a society that thrives on unity.
The Necessity of Good Manners
 Inherent in every civilized society, good manners signify an individual’s upbringing and understanding of the surrounding world. As living embodiments of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah, people with good manners display an innate respect for the settings in which they interact. Their consideration for the comfort, feelings, or preferences of others translates into thoughtful actions and courteous speech. For instance, simple actions like saying “please” or “thank you,” respecting personal space, or displaying patience towards others represent such behavior.
Inherent in every civilized society, good manners signify an individual’s upbringing and understanding of the surrounding world. As living embodiments of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah, people with good manners display an innate respect for the settings in which they interact. Their consideration for the comfort, feelings, or preferences of others translates into thoughtful actions and courteous speech. For instance, simple actions like saying “please” or “thank you,” respecting personal space, or displaying patience towards others represent such behavior.
Respect and Politeness as Social Norms
 Respect and politeness form the bedrock of societal norms. They create an environment where individuals feel valued and safe. The manifestation of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah reflects in treating each individual with dignity, regardless of their status. It’s observed in having the decorum to handle disagreements in an agreeable manner, maintaining a respectful tone of voice, or giving others the chance to express themselves. These norms promote a sense of social responsibility and contribute to positive societal relationships.
Respect and politeness form the bedrock of societal norms. They create an environment where individuals feel valued and safe. The manifestation of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah reflects in treating each individual with dignity, regardless of their status. It’s observed in having the decorum to handle disagreements in an agreeable manner, maintaining a respectful tone of voice, or giving others the chance to express themselves. These norms promote a sense of social responsibility and contribute to positive societal relationships.
By integrating these values into their conduct, individuals not only make a societal impact, but also develop personally. Through a respectful and polite demeanor, they establish a reliable reputation, gain trust, and foster mutual respect in their relationships. Hence, the habit of adhering to societal manners and norms, encapsulated in the principle of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah, holds pivotal importance in any society.
Case Studies of Contoh Penerapan Tata Krama Dalam Bersikap Adalah
This section unfolds the mysterious concept of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah through an exploration of case studies from across the globe. It digs deeper into the core of this Indonesian principle and its practical applications, rooted in real-life examples and cross-cultural dynamics.
Real-life Application Examples in Different Countries
 Take a global tour and discover the enchanting realm of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah in various nations. For instance, in Japan, you’ll find ‘Keigo,’ a meticulously defined etiquette system built around respect for others. Similarly, the German culture reveres ‘Höflichkeit,’ denoting a civil and respectful demeanor. Look to South Korea, and there’s ‘Chaemyeon,’ a social norm that acknowledges the importance of maintaining a proper image and respect in public.
Take a global tour and discover the enchanting realm of contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah in various nations. For instance, in Japan, you’ll find ‘Keigo,’ a meticulously defined etiquette system built around respect for others. Similarly, the German culture reveres ‘Höflichkeit,’ denoting a civil and respectful demeanor. Look to South Korea, and there’s ‘Chaemyeon,’ a social norm that acknowledges the importance of maintaining a proper image and respect in public.
Cultural Differences and Similarities in Application
Though the term contoh penerapan tata krama dalam bersikap adalah is inherently Indonesian, its essence resonates across cultures, encapsulating a universal tenet of respect and courtesy. Yet, it’s fascinating to see how diverse cultures interpret and implement this fundamental principle. While Japanese ‘Keigo’ emphasizes humility, German ‘Höflichkeit’ prioritizes straightforwardness, and South Korean ‘Chaemyeon’ considers the public image.